Project 1 VMSpring 2026
The Application Security project requires a specific architecture (x86_64) and specific kernel changes, meaning that it requires a virtual machine (VM). You can control the VM either via a terminal or via SSH, which allows a text editor like VS Code to be used in remote mode on your local machine. The project must be completed within this VM. Do not update the software in the VM! Doing so may change the behavior of your project code.
It is your responsibility to set enough disk space aside on your personal device
for all course material, including this VM, and to make regular backups of your data
(snapshots in VirtualBox will be covered subsequently in this tutorial). If disk
space is scarce, you may want to consider migrating your data to the cloud
(Georgia Tech provides 1 TB of OneDrive storage to every student through your gatech.edu email),
or to an external storage medium. Except in the most extenuating circumstances, the course staff are not able to
provide accommodations due to a lack of space and/or loss of data.
Last but not least, if you run into any problems while reading this guide, there are a number of sections addressing troubleshooting at the bottom of this document. We will update this document continually as we encounter new problems or parts where many people are struggling on.
This guide is split up based on your host operating system. Navigate to the relevant section: Windows and Linux hosts, and macOS hosts.
Setup
Windows and Linux Hosts Install
Step 1 - Download the VM and VirtualBox
Download the VM appliance (cs3235appsecvm.ova) from here.
You will use VirtualBox to run the aforementioned VM. Download the latest version for your host operating system here.
Step 2 - Import the VM Appliance
In VirtualBox’s main menu, navigate to Tools, and then Import. Select the
VM appliance file (cs3235appsecvm.ova) which you downloaded, and continue to click
the Next button until you are no longer prompted; you do not need to modify
any settings. Simply verify that your default settings look like the image below:
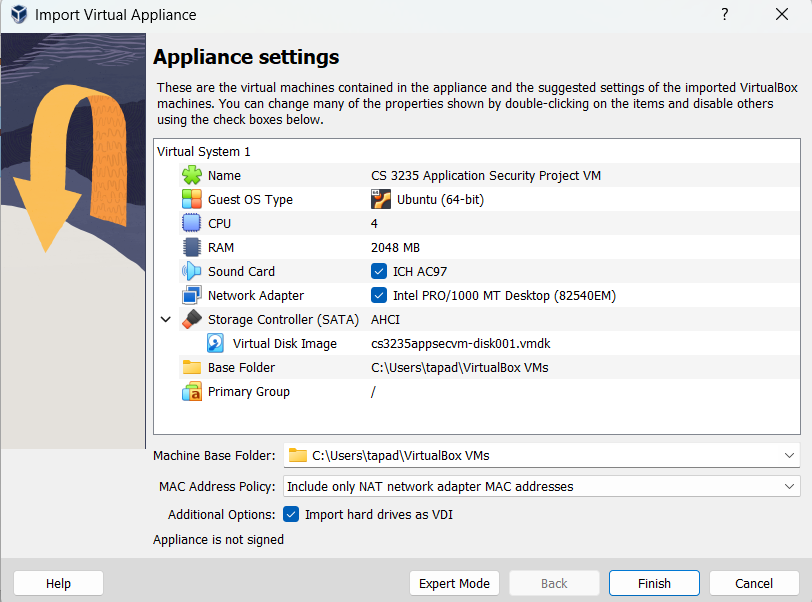
The import process may take several minutes. Once complete, run the VM. After clicking start, the start button should switch to “Show”—this is expected! Because the VM is intended to be connected to via SSH, no window opens up for it by default (“headless” mode); it is simply running in the background (“Show” can be used if you need to debug the SSH connection).
Once you’ve successfully installed the VM, continue on to the Workflow section!
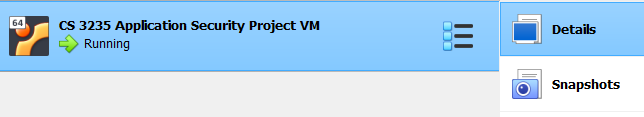
Optional - Take a Snapshot
VirtualBox snapshots allow you save the state of your VM at a point in time. From the VirtualBox manager, select Snapshots as shown in the image below. In the panel that appears, click Take to save a snapshot; should you make an irrevocable mistake, you can always revert to this initial snapshot instead of downloading the VM appliance again (just note that any files created or edited in the VM since the last snapshot will be lost.)
macOS Hosts Install
This install method works on both Intel and Apple Silicon Macs.
Step 1 - Download the VM and UTM
Download the VM appliance (cs3235appsecvm.zip) from here.
On macOS, we will use a program called UTM to run the VM. Download UTM from here and move the application to your Applications folder for future use.
Step 2 - Import the VM Appliance
Double click the CS 3235 Application Security Project VM.utm file in your Finder
(you may need to extract it from the .zip manually depending on the browser you’re using),
which should open UTM to a screen similar to the following:
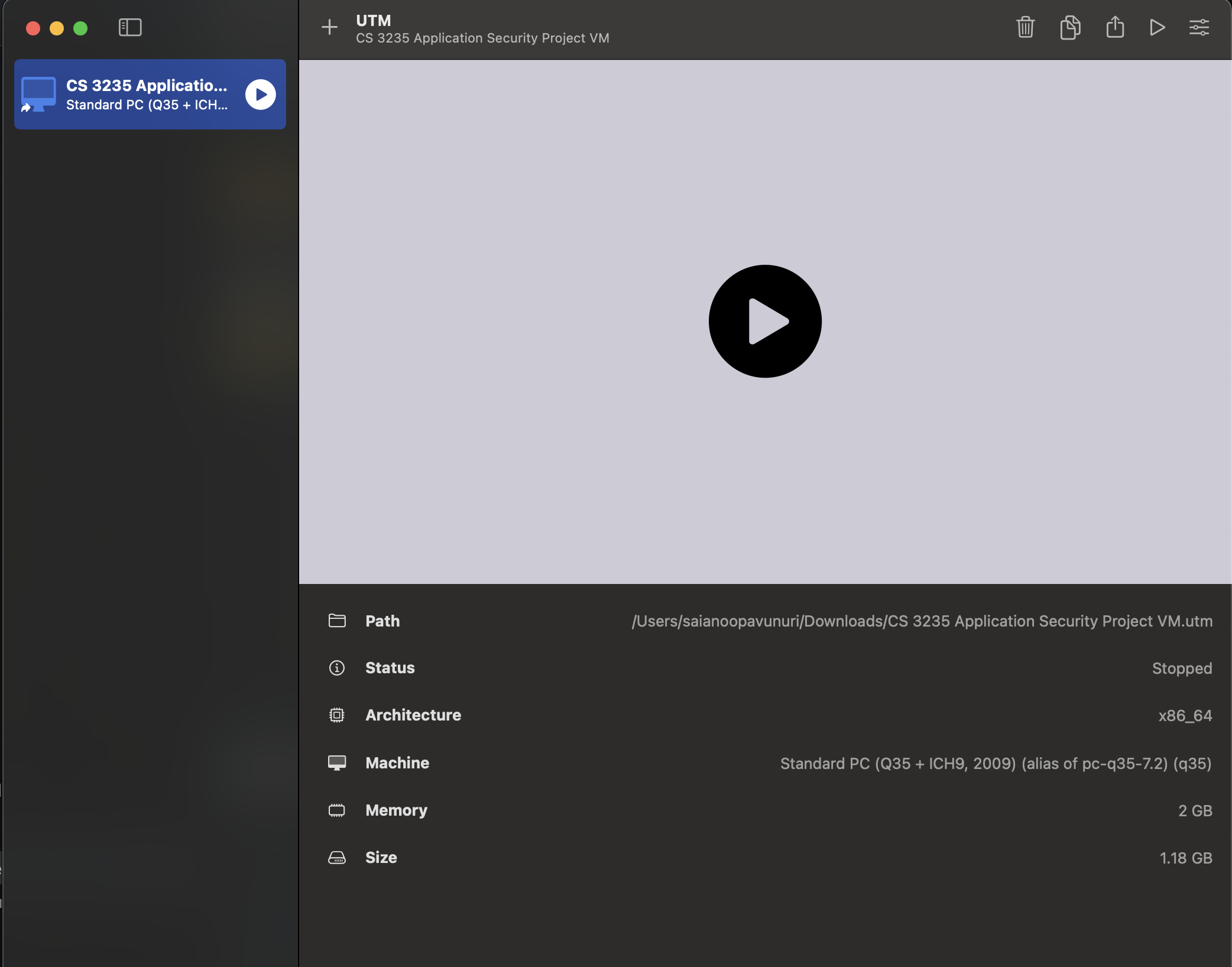
The architecture being x86_64 is expected, even if you are on an Apple Silicon Mac! This is the architecture of the virtual machine, which will always be based on x86.
After clicking run (any of the three play buttons found in the above screenshot will work), you will see some text flash across the screen; after a few seconds, you should be greeted with a login prompt. You are now safe to minimize this window, but do not close it—UTM unfortunately does not feature headless support like VirtualBox. This window will need to remain open, even if in the background, while you are working.
Workflow
The preferred code editor for this course is Visual Studio Code (VS Code). If you’re not familiar, VS Code is a very powerful and lightweight code editor from Microsoft. It is available to download for free from here for Windows, Linux, and macOS hosts. You will use VS Code’s SSH extension to connect and work on the VM remotely. Similarly, in upcoming projects, you will use VS Code’s Dev Containers extension with the project’s respective Docker containers. This will enable you to work on your projects as if they’re natively running on your machine while seamlessly integrating the VM or container in the background. As an added advantage, it also lets us, the course staff, ensure that all students have access to the same standardized environment.
The VM is set up to automatically open port 3235 on your host at which its SSH server can be reached, meaning that we can easily connect VS Code to the VM and work within it:
If you’re working on a Windows host and have WSL 2 enabled, first run VS Code within Windows rather than within WSL 2 by clicking on the remote icon in the bottom left and choosing “Remote-WSL: Reopen Folder in Windows”. This is because WSL 2 runs in a VM of its own, and cannot access services run in the Windows host by default.
-
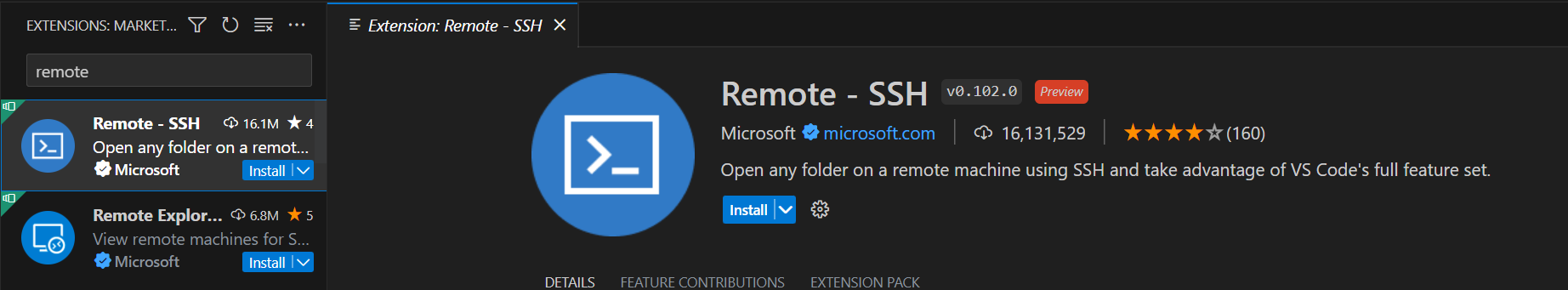
Inside VS Code, search the extensions marketplace for “Remote - SSH” and install the extension if you haven’t already done so.
-
Next, open the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P on Windows and Linux, ⌘+⇧+P on macOS) and search for “Remote-SSH: Connect to Host”. A dialog will appear asking where you want to connect—enter
cs3235@localhost:3235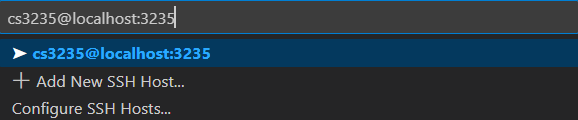
If you’re presented with the VM’s SSH fingerprint, select Continue. If you’re asked for the operating system of the remote, select Linux.
Setting up the VM as a persistent host in VS Code can be convenient, but the syntax to do so is different. If you select “Add New SSH Host”, you’ll see that VS Code prompts you to enter the SSH Connection Command, which in this case is
ssh cs3235@localhost -p 3235, rather than using thehost:portsyntax of the “Connect to Host” prompt. -
The window should exit and re-open shortly, at which point you’ll be prompted for a password. This is the password for the
cs3235user, which iscs3235. Once you enter it, your VS Code window will now be connected to the VM! Note that the VM will prompt for thecs3235password in the palette command dialog box every time you open the VS code window. You should see “SSH: localhost:3235” in the bottom left corner of the window. You might now want to install any extensions that you have in your local VS Code instance into the VM—open the command palette once again and search for “Remote: Install Local Extensions in…”, select the box at the top to select all extensions, and install.
You should now essentially feel exactly like you’re developing on your local machine with the same settings and extensions, while you’re actually in the VM! For example, here is what you might see after opening a terminal and seeing what folder we’re in:
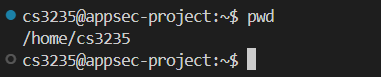
With user cs3235 and folder /home/cs3235, it’s clear that our
VS Code instance is connected to the VM.
You are now able to do your work within VS Code and its terminal view, and can also copy files from your host into the VM with a simple drag into the window. You are also free to work over classical SSH in a terminal or even in the VM window, but we think that this workflow should be the most comfortable at this point in the course.
If you mistakenly clone your starterfiles to your host OS and then try to drag-and-drop them into the VM using VS Code, your files’ permissions will be reset. This can have unexpected consequences and is not recommended. Instead, clone your starterfiles directly in the VM using the procedure described in the Git guide.
Tips & Troubleshooting
If everything works well so far, you’re all set — no need to scroll further down in this document. However, if that is not the case, you might find the following helpful.
Download files from the VM
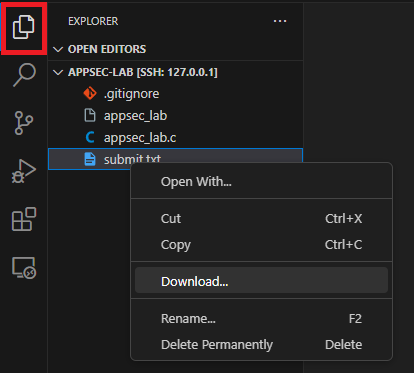
If you want to transfer files from the VM to your host OS — let’s say to submit them to the autograder for grading, VS Code provides an easy way to do so.
In the Explorer view, simply right click on the file that you want to transfer from the VM to your host OS and select “Download…”. If you want to transfer multiple such files, hold Ctrl (on Windows and Linux) or ⌘ (on macOS), click on all the files you want to transfer, right click, and select “Download…”.
Remote SSH connection error
If you get an error ‘Could not connect to host’, please restart VS code and try connecting again.
CPU Virtualization
VirtualBox requires an x86(-64) processor with hardware-assisted virtualization; such feature is called VT-x on Intel processors and AMD-V on AMD processors. If you have a Mac, virtualization should be enabled by default in firmware. If you have a PC, chances are the feature will be enabled from the factory, yet this is not always the case.
In order to enable virtualization, you will need to enter the setup menu of your BIOS or UEFI on your PC. The key combination to press immediately after startup differs by PC manufacturer, but oftentimes it is one of F2, Delete, F10, F12, or Esc. Consult your manufacturer’s documentation if you are unsure. The location of the setting will also differ by manufacturer. However, the name will almost always include ‘virtualization’ or ‘virtualization technology’.